In the dynamic field of MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) engineering, hiring the right talent requires more than looking at resumes. Technical proficiency, problem-solving skills, and the ability to apply knowledge effectively are critical for engineers designing and maintaining complex building systems. This article explores three practical technical tests to help identify top MEP engineers during interviews, ensuring a more robust evaluation process.
1. Technical Test 1: Design Problem Solving
Candidates can be presented with scenarios mirroring real-world challenges to effectively assess problem solving skills and technical knowledge in MEP systems design. Let’s find out how candidates might approach designing a sustainable HVAC system for a LEED-certified office building in a hot climate zone.
Scenario: Designing a Sustainable HVAC System for a LEED-Certified Office Building
1. Approach to Selecting Equipment
Understanding Cooling Load Calculation: Conduct thorough calculations to determine the building’s cooling load requirements. This involves analyzing building orientation, insulation levels, occupancy, fluid mechanics, and internal heat gains from equipment and lighting. Candidates should demonstrate numerical calculation skills and an understanding of fundamental ideas in HVAC design.
Equipment Selection Based on Efficiency Ratings (SEER, EER): Choose HVAC equipment with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio(SEER) and Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) ratings. These metrics indicate how efficiently the equipment operates under typical conditions, ensuring optimal energy performance and cost savings over time.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Explore opportunities to integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar or geothermal energy, into the HVAC system design. This will reduce the building’s carbon footprint and align with LEED requirements for sustainable design practices.
2. Calculating Cooling Load
Load Calculation Methodology: Use industry-standard methodologies like the ASHRAE Handbook or software tools such as TRACE 3D Plus to calculate cooling loads accurately. This involves accounting for factors like external climate conditions, internal heat gains, ventilation requirements, and thermal properties of building materials.
Optimizing Ductwork Design: Design efficient ductwork layouts to minimize pressure losses and ensure uniform air distribution throughout the building. This includes selecting appropriate duct sizes, optimizing airflow velocities, and positioning duct runs to reduce energy losses.
3. Evaluation Criteria
Candidates will be evaluated based on their proficiency in:
Accurate Cooling Load Calculations: Demonstrating a thorough, solid understanding of load calculation methodologies and applying them effectively.
Equipment Selection: Choosing HVAC equipment with high SEER and EER ratings appropriate for the building’s requirements.
Integration of Sustainability Practices: Incorporating renewable energy sources and meeting LEED energy efficiency and sustainability requirements.
Technical Test 2: Code Compliance and Standards
Objective: Assess candidates’ knowledge and application of building codes and MEP standards, explicitly focusing on electrical and plumbing systems.
Example Scenario: Imagine you are reviewing plans for a hospital renovation project in a major city. Your task is to identify potential electrical and plumbing code violations according to NEC (National Electrical Code)and IPC (International Plumbing Code) standards. Propose solutions that prioritize safety and compliance with local regulations.

Evaluation Criteria: Candidates will be evaluated based on their ability to identify code violations related to electrical systems (electrical circuits) and plumbing installations (IPC). The solutions proposed should demonstrate a clear understanding of safety measures and compliance requirements. This will include communication skills, as they must clearly articulate their findings and solutions.
Technical Test 3: Simulation or Modeling Exercise
The simulation or modeling exercise assesses candidates’ proficiency using technologies of MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) simulation or modeling software, such as Revit MEP. This test provides insights into their ability to simulate complex scenarios and propose practical design solutions.
Example Scenario
Candidates are tasked with using Revit MEP software to simulate airflow dynamics in a high-rise residential building. The objective is to optimize the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system layout to maximize energy efficiency and indoor air quality. They are expected to analyze airflow patterns, propose adjustments to ductwork layout, and position equipment strategically to achieve optimal results.
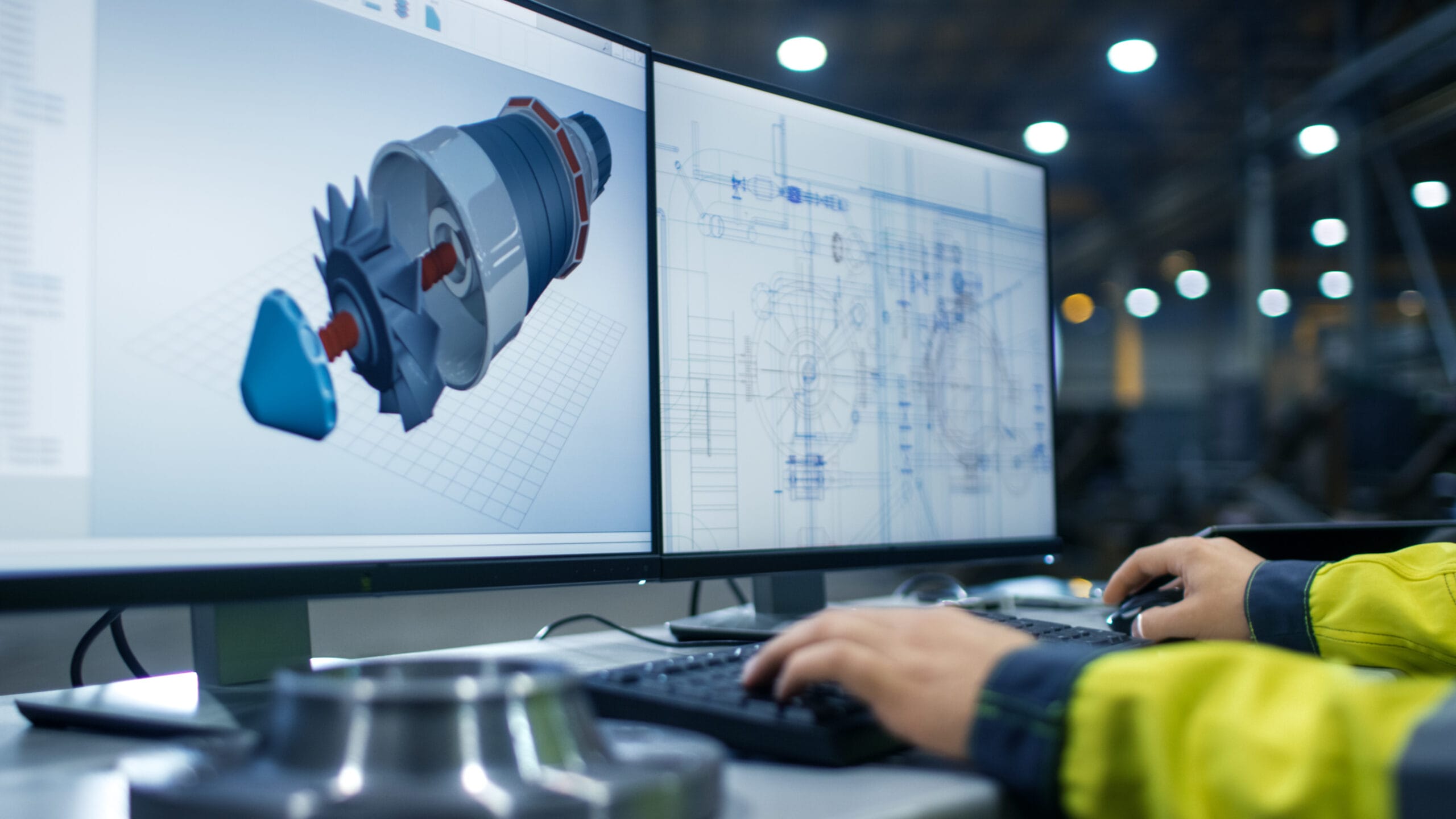

Evaluation Criteria
Proficiency in Revit MEP: Candidates should demonstrate high competence in navigating and effectively using Revit MEP tools.
Simulation Accuracy: Accuracy in simulating airflow dynamics and predicting indoor air quality improvements is crucial.
Design Optimization: Candidates should propose design improvements based on simulation results to minimize energy consumption while enhancing indoor comfort levels.
Integration with Interview Process
To seamlessly integrate technical tests into the interview process following MEP engineer interview questions, follow these practical steps:
1. Scheduling and Preparation
Allocate sufficient time for candidates to complete the technical tests without rushing. Provide clear instructions on what they must accomplish and how their performance will be evaluated. This clarity helps candidates understand the expectations and perform their best during the assessment.
2. Holistic Evaluation
Combine the results from mechanical engineering tests with insights gained from traditional interviews. This dual approach allows you to assess candidates comprehensively. Look beyond technical skills to evaluate problem-solving abilities and how well candidates fit into your organizational culture. This holistic evaluation ensures that you’re hiring for technical proficiency and overall compatibility with your team and company values.
3. Providing Constructive Feedback
After candidates complete the tests, offer constructive feedback regardless of whether they are selected for the role. Based on their test performance, highlight their strengths and provide actionable insights into areas where they can improve. This feedback helps candidates understand their standing and positively reflects your company’s commitment to transparency and development.
4. Enhancing Hiring Decisions
By integrating technical tests into your interview process, you enhance the accuracy of your hiring decisions. These tests provide tangible evidence of candidates’ abilities beyond what resumes can convey. This approach ensures that you’re selecting candidates who meet the role’s technical demands and demonstrate the problem-solving skills and software proficiency needed to excel in their positions.
Advantages of Technical Tests
Using technical tests during the hiring process provides significant advantages that traditional resume reviews alone cannot offer. Here’s why they are valuable:
1. Objective Assessment of Technical Skills
Technical tests offer a fair and transparent way to evaluate candidates’ technical abilities. Unlike resumes that might exaggerate skills or lack details, tests require candidates to demonstrate what they know and can do in real-world situations. This ensures hiring decisions are based on solid proof of skills rather than paper claims.
2. Identification of Practical Problem-Solving Abilities
These tests present candidates with real-life challenges similar to those they would face on the job. This practical approach helps employers see how candidates approach problems, suggest solutions, and use their technical knowledge effectively. It also gives insights into candidates’ thinking processes and decisions when faced with challenges, which are crucial in technical and engineering roles.
3. Software Proficiency Evaluation
Many technical tests assess candidates’ familiarity with software tools and platforms used in the job, like CAD software, programming languages, or simulation tools. Evaluating these skills ensures that candidates can handle tasks efficiently from the start. It also helps employers gauge how experienced candidates are with specific software, which is crucial for technical roles in MEP projects.
4. Enhanced Confidence in Hiring Decisions
By adding technical tests to interviews and resumes, employers get a more complete picture of each candidate’s abilities. This thorough evaluation reduces the risks in hiring by confirming candidates’ skills through practical tests. It boosts confidence in hiring choices, ensuring that the selected candidates not only meet but exceed the technical requirements of the position.
Using technical tests is an effective way for companies to ensure they hire the best candidates for technical roles. It provides a clear view of candidates’ capabilities, problem-solving skills, and proficiency with necessary software tools. This approach leads to better hiring decisions and stronger teams that effectively meet the company’s technical demands.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, incorporating technical tests into MEP engineering test interviews is essential for identifying top talent capable of delivering innovative, compliant, and efficient solutions. By assessing candidates’ problem-solving abilities, code compliance knowledge, and proficiency with simulation tools, firms can make informed hiring decisions that drive project success and client satisfaction following industry trends.
This approach ensures that MEP firms attract and retain MEP engineers who meet and exceed expectations in today’s competitive engineering landscape by leveraging real case studies and practical examples. Start your journey today and prepare technical tests with Network Mountain.
